Imagine stepping into your garden, the air fragrant with lavender, mint, and tulsi, as the leaves glisten in the sunlight. A medicinal plant garden offers more than just beauty—it’s a gateway to natural remedies and holistic living. However, the secret to such a thriving sanctuary lies beneath the surface: healthy soil and the right fertilizers.
A thriving medicinal plant garden begins with one key ingredient: healthy, nutrient-rich soil. Whether you’re growing basil for tea or echinacea for immune support, ensuring the right balance of organic nutrients and fertilizers is essential. This guide will help you understand soil health, choose the best organic nutrients for outdoor growth, and explore practical methods for fertilizing medicinal plants to ensure they flourish

Table of Contents
The Impact of Fertilizers on Medicinal Plant Garden Growth
Medicinal plants derive their healing properties from the nutrients they absorb from the soil. A well-nourished plant has higher concentrations of beneficial compounds like alkaloids, essential oils, and antioxidants. However, nutrient deficiencies can lead to stunted growth and reduced potency
Understanding Nitrogen in Soil
Nitrogen is a critical nutrient for plant growth, contributing to leafy foliage and overall vitality. But many medicinal plants suffer in nitrogen-poor soil or when there’s no nitrogen in soil at all.
5 Ways to Add Nitrogen to Soil
- Use worm castings for weed and medicinal plants, as they are rich in nitrogen and beneficial microbes.
- Incorporate compost fertilizer for plants to improve soil structure and nutrient content.
- Try planting nitrogen-fixing cover crops, like clover, as a natural way to get nitrogen in soil.
- For immediate results, apply urea nitrogen for plants, a fast-releasing fertilizer.
- Adding nitrogen to soil naturally with kitchen scraps or coffee grounds is eco-friendly and effective.
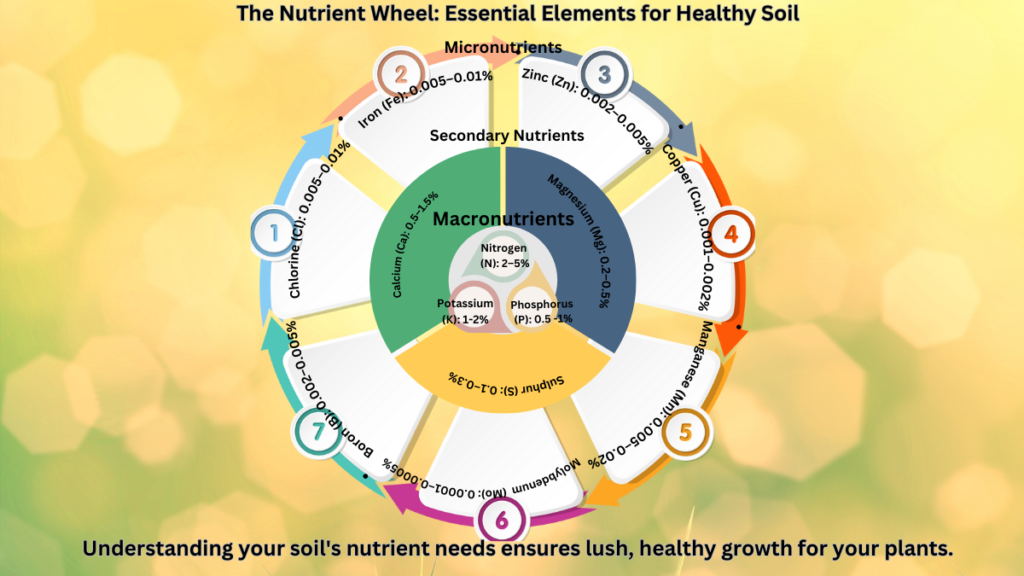
How to Choose the Right Fertilizer for Medicinal Plant Gardens?
Medicinal plants thrive on fertilizers that balance macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) with trace minerals like calcium and magnesium.
Best Organic Nutrients for Outdoor Grow
- Bone meal: Rich in phosphorus, it’s excellent for root development. Start by adding bone meal to soil before planting.
- Calcium sulfate fertilizer: Ideal for improving soil structure and boosting calcium levels in medicinal plants.
- Ground fertilizer: Use rock dust or greensand for long-lasting potassium supply.
Best Organic Fertilizers for Indoor Plants and Herbs
- Best organic fertilizer for indoor plants: Use liquid fertilizers like compost tea or diluted fish emulsion for even nutrient distribution without overloading the soil.
- Best organic fertilizer for herbs: Opt for nutrient-rich worm castings or a balanced organic fertilizer to support flavorful and aromatic herb growth.
- Best fertilizer for kitchen garden: A balanced NPK fertilizer enriched with micronutrients like iron and zinc.
4 DIY Fertilizer Solutions for Medicinal Plants
Creating your own fertilizers at home is cost-effective, eco-friendly, and ensures you know exactly what your plants are absorbing. Here are some easy DIY recipes to boost your medicinal plants’ health.
1.Acidic Fertilizer Homemade
Some medicinal plants, like chamomile and lavender, thrive in slightly acidic soil. Here’s a simple recipe to create an acidic fertilizer:
- Collect used coffee grounds and mix them with water to create a slurry.
- Add crushed eggshells to provide calcium.
- Apply this mixture as a soil drench once every two weeks to balance soil acidity and feed your plants.
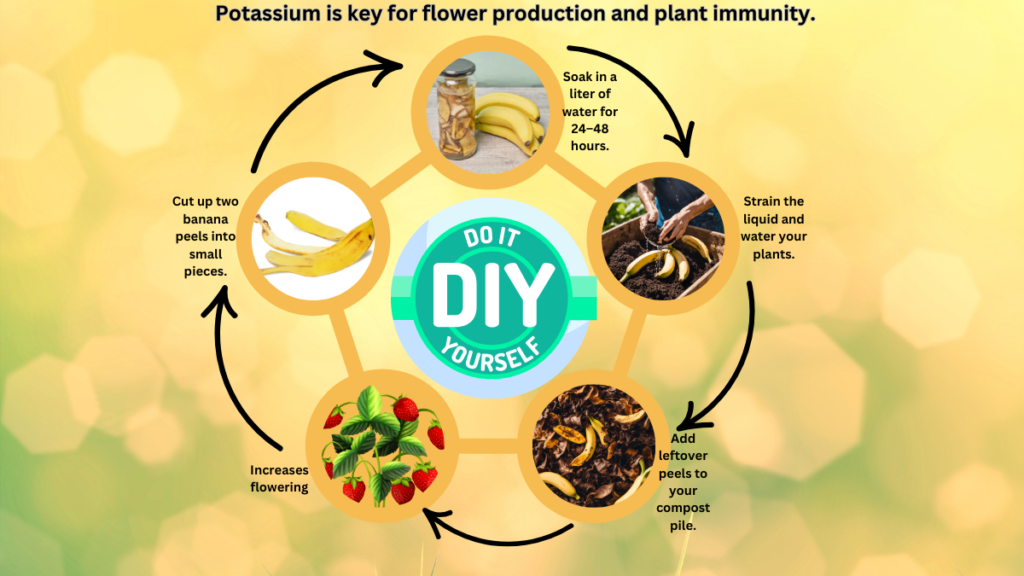
2.Banana Peel Tea for Potassium
Potassium is essential for flower production and plant immunity. This easy banana peel tea works wonders for medicinal plants like calendula and dandelion.
- Cut up two banana peels into small pieces.
- Soak them in a liter of water for 24–48 hours.
- Strain the liquid and use it to water your plants. The leftover peels can be added to your compost pile.
3.Fish Emulsion Fertilizer
Rich in nitrogen and trace minerals, fish emulsion is an excellent fertilizer for leafy medicinal plants such as holy basil or mint.
- Collect fish scraps (heads, bones, etc.) and blend them with water in a ratio of 1:2.
- Let the mixture sit in an airtight container for about two weeks, stirring occasionally.
- Dilute the liquid (1 part emulsion to 10 parts water) before applying it to the soil.
4.Compost Fertilizer for Plants
Composting is one of the most sustainable ways to feed your medicinal plants. Follow these steps for a balanced compost pile:
- Layer “greens” (vegetable scraps, coffee grounds) with “browns” (dried leaves, cardboard).
- Keep the pile moist but not soggy.
- Turn it regularly to ensure proper aeration.
- In 6–8 weeks, you’ll have nutrient-rich compost to amend your soil or top-dress your plants.
2 Steps to Installing Fertilizers of Medicinal Plant Garden
Applying fertilizers effectively is as important as choosing the right type.
1.Adding Fertilizer to Soil in Garden Beds
- Till soil lightly to mix in nutrients before planting.
- For established plants, use side-dressing or top-dressing methods to minimize root disturbance.
2.Adding Nitrogen to Plants Naturally
If your medicinal plants show signs of nitrogen deficiency (yellowing leaves), try this:
- Add a mulch layer of alfalfa or grass clippings.
- Apply compost tea rich in nitrogen to the soil.
Step-by-Step Guides for Soil Testing and Fertilization
Healthy soil is the foundation of successful gardening. Here’s how to test and amend your soil effectively:
1.Testing Soil pH and Amending It
Soil pH determines the availability of nutrients for plants. Most medicinal plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0–7.0).
Step 1: Test Your Soil
- Purchase a soil pH test kit from a garden center or online.
- Collect soil samples from different areas of your garden.
- Mix each sample with distilled water as per the kit instructions and check the pH reading.
Step 2: Amend Your Soil
- If the soil is too acidic (low pH), add lime or wood ash.
- If it’s too alkaline (high pH), amend it with sulfur or organic matter like pine needles.
- Retest the soil after 2–4 weeks to ensure the amendments have worked.
2.Creating Balanced Compost Piles
Compost is only as good as the ingredients you use. Follow these steps to create nutrient-dense compost:
- Begin with a base layer of “browns” like dried leaves, shredded newspaper, or sawdust.
- Add a layer of “greens” such as fruit and vegetable scraps, grass clippings, or coffee grounds.
- Maintain a ratio of about 2 parts brown to 1 part green for optimal decomposition.
- Sprinkle some soil or finished compost on each layer to introduce beneficial microbes.
- Water lightly after each layer to keep the pile damp but not soggy.
- Turn the pile every 1–2 weeks to ensure even decomposition and airflow.
By using these DIY solutions and effective soil preparation techniques, you’ll give your medicinal plants the best possible start while keeping your gardening sustainable.
FAQ
What is the ideal NPK ratio for growing herbs?
The ideal NPK ratio for herbs is 3-1-2 or 4-1-2, promoting leafy growth while supporting root health and overall plant vitality.
How often should I fertilize my herbs?
Fertilize herbs every 4–6 weeks during their growing season, using a balanced or slightly nitrogen-rich fertilizer.
Are chemical fertilizers safe for herbs?
While chemical fertilizers can work, organic options are safer for edible herbs to avoid chemical residues.
Should I fertilize indoor herbs differently from outdoor ones?
Yes, indoor herbs benefit from diluted liquid fertilizers applied every 2–4 weeks to prevent over-fertilization.
Can herbs grow in poor soil?
Herbs can grow in less fertile soil but thrive better with nutrient-rich amendments like compost or organic fertilizers.
Conclusion
Healthy soil and appropriate fertilization are the cornerstones of a thriving medicinal plant garden. Whether you’re using worm castings for weed, applying compost fertilizer for plants, or experimenting with acidic fertilizer homemade, understanding your plants’ needs ensures better growth and higher potency. Start small, observe your garden, and fine-tune your approach to create a sustainable, nutrient-rich environment for your medicinal plants.
By investing in soil health and organic fertilizers, you not only enhance the growth of your medicinal plants but also contribute to a greener, healthier environment.
To ensure your planting efforts yield the best results, having the right tools is essential—give it a read here to explore gardening tools that make planting easier and more efficient!
Disclaimer: TThe information provided in this blog is for educational and informational purposes only. While we strive to ensure accuracy, always consult a local gardening expert or professional before applying fertilizers or making soil amendments. Individual plant needs and environmental conditions may vary, so use this advice as a general guideline. We are not responsible for any damage or outcomes resulting from the use of the information provided here. Always handle fertilizers with care and follow manufacturer instructions.

I’m a passionate advocate for natural wellness, specializing in the health benefits of medicinal plants. I explore how traditional and modern practices merge to harness the power of plants. My focus lies in educating others about the therapeutic properties of herbs and flowers, aiming to make plant-based remedies accessible and practical. Through my content, I hope to inspire a deeper appreciation for nature’s role in promoting well-being and sustainable health practices.
