Imagine walking through a garden filled with the soothing scent of lavender, its delicate purple blooms swaying gently in the breeze. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, English Lavender can add a touch of tranquility and beauty to your outdoor space. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about growing and enjoying this wonderful plant. Let’s dive into the world of English Lavender, discover its varieties, learn some handy growing tips, and uncover its amazing benefits.
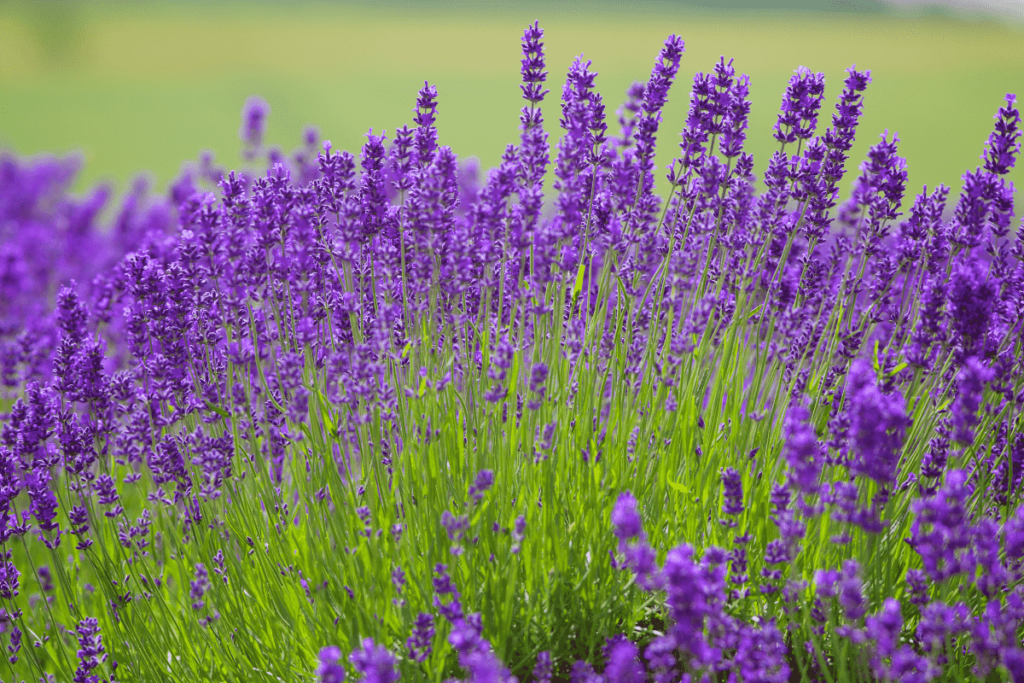

Table of Contents
English Lavender Plant
English Lavender, known scientifically as Lavandula angustifolia, is a beloved herb cherished for its fragrant flowers, hardy nature, and versatility in gardens and landscaping. This beautiful plant, native to the Mediterranean, is renowned for its calming scent and numerous uses, making it a popular choice for gardeners around the world. In this article, we will delve into the essentials of growing It, explore the varieties available, provide insights into its seeds, and highlight its myriad benefits.
Overview of English Lavender
English Lavender is a hardy perennial that thrives in well-drained soil and full sun. It is distinguished by its narrow leaves and spikes of small, aromatic flowers that bloom in shades of purple, blue, and occasionally white. One of the key characteristics of this is that apart from other types, such as French Lavender (Lavandula dentata), is its superior cold tolerance, making it suitable for a wider range of climates.
Varieties of English Lavender
There are several popular varieties of English Lavender, each with unique characteristics:
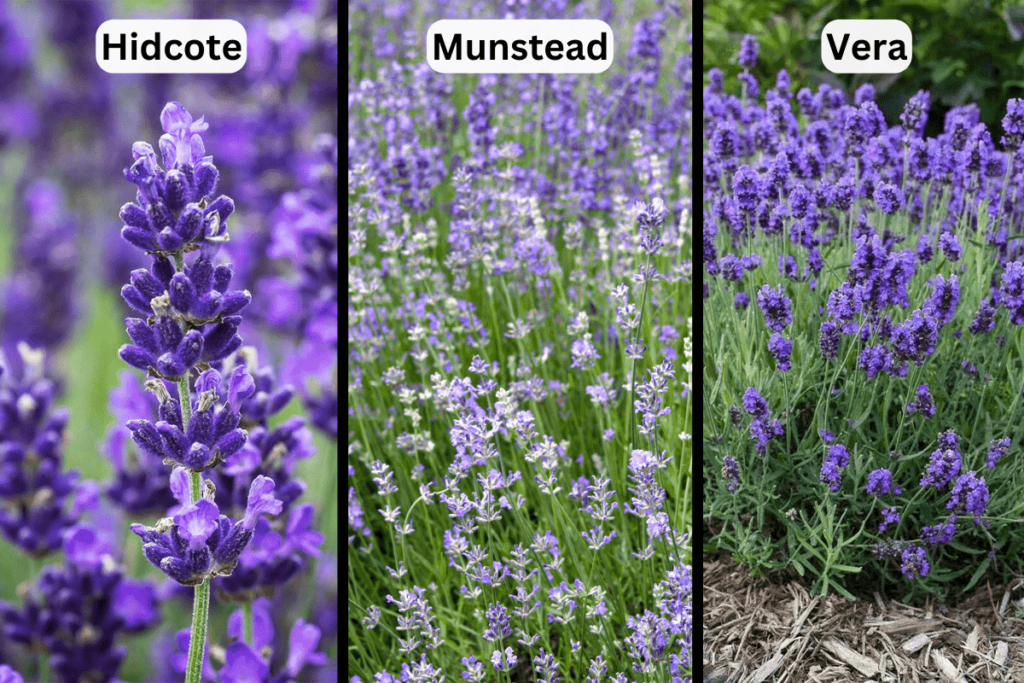

- Hidcote: Known for its deep purple flowers and compact growth, making it ideal for borders and hedges.
- Munstead: A versatile variety with light purple flowers, valued for its hardiness and fragrant blooms.
- Vera: Often considered the true English Lavender, it has tall spikes and a strong aroma, perfect for essential oil production.
Growing Tips for English Lavender
Growing English Lavender successfully requires attention to a few key factors:
Soil and Location
- Soil: Ensure the soil is well-drained, as Lavender does not tolerate waterlogged conditions. Sandy or gravelly soil with a neutral to slightly alkaline pH is ideal.
- Location: Plant in a spot that receives full sun for at least six hours a day. Good air circulation is also crucial to prevent fungal diseases.
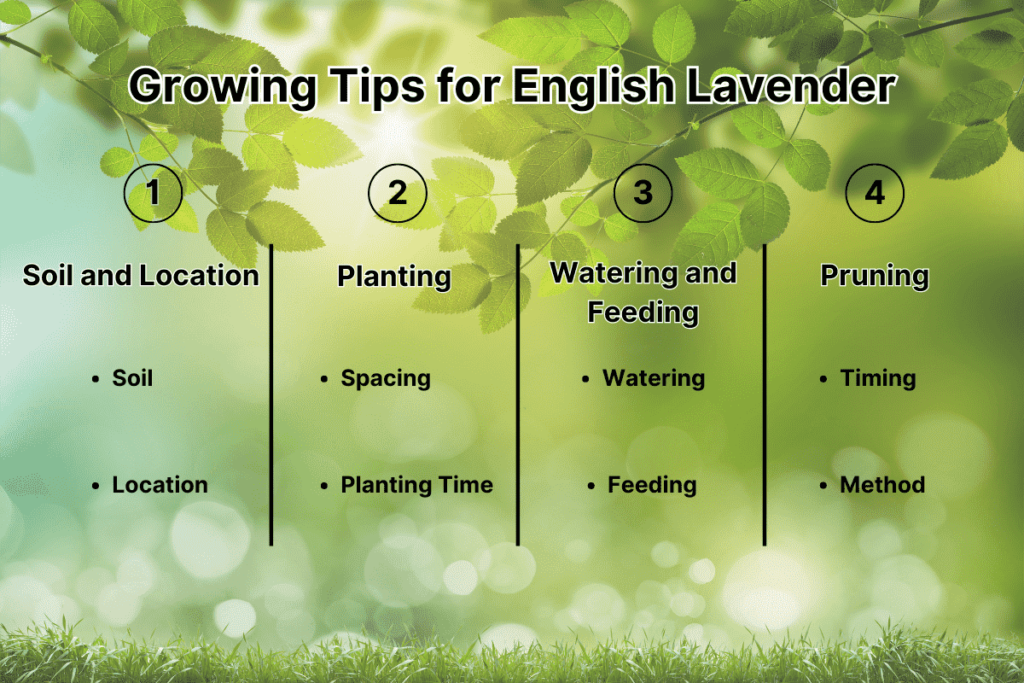
Planting
- Spacing: Space plants about 12 to 18 inches apart to allow for air circulation and growth.
- Planting Time: The best time to plant Lavender is in the spring after the danger of frost has passed or in the fall in warmer climates.
Watering and Feeding
- Watering: Water newly planted Lavender regularly until established. Once mature, Lavender is drought-tolerant and should be watered sparingly.
- Feeding: Lavender does not require heavy feeding. A light application of compost in the spring is usually sufficient.
Pruning
- Timing: Prune Lavender annually in late summer or early fall after flowering.
- Method: Cut back about one-third of the plant’s growth to encourage a compact shape and prevent woody stems.
English Lavender Seeds
Growing it from seeds can be a rewarding experience, offering the satisfaction of nurturing this beautiful plant from its earliest stages. When choosing to grow English Lavender from seeds, it’s important to select high-quality seeds from a reputable source to ensure healthy and robust plants. Here are some key points to consider when working with English Lavender seeds:
Seed Selection and Preparation
- Quality Seeds: Purchase seeds from a trusted supplier to ensure they are viable and true to type.
- Stratification: Some gardeners recommend cold stratification for Lavender seeds. This process involves placing the seeds in a damp paper towel, sealing them in a plastic bag, and refrigerating them for about 4-6 weeks to simulate winter conditions, which can enhance germination rates.
Sowing and Germination
- Seed Starting Mix: Use a light, well-draining seed starting mix. Fill seed trays or small pots with the mix and lightly water it.
- Sowing: Scatter the seeds on the surface of the soil and gently press them in. Cover the seeds lightly with a thin layer of the seed starting mix or fine sand.
- Light and Temperature: Place the trays or pots in a bright location with indirect sunlight. Lavender seeds require warmth to germinate(18-21°C) is ideal.
Care and Maintenance
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Using a spray bottle can help provide gentle and even moisture.
- Germination Time: Be patient, as Lavender seeds can take anywhere from 2 to 4 weeks to germinate. It’s important to maintain a consistent environment during this period.
Transplanting Seedlings
- First Leaves: Once the seedlings have developed a few sets of true leaves, they are ready to be transplanted.
- Hardening Off: Gradually acclimate the seedlings to outdoor conditions by placing them outside for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the time over a week or two.
- Planting Outdoors: Choose a sunny spot with well-drained soil for transplanting. Space the plants about 12 to 18 inches apart to ensure good air circulation and room for growth.
Growing this from seeds can be a rewarding and cost-effective way to fill your garden with this fragrant, beautiful plant. With patience and proper care, you’ll soon enjoy the sight and scent of blooming lavender in your garden.
Also Read:
Discover the Power of False Daisy: 5 Amazing benefits and medicinal uses
5 Health Benefits of Java Plum (Jamun) – An Amazing powerhouse
Benefits of English Lavender
English Lavender is prized for its wide range of benefits, making it a valuable addition to any garden:
- Aromatherapy and Relaxation: The calming scent of Lavender is widely used in aromatherapy to reduce stress and promote relaxation. Lavender oil and dried flowers can be used in sachets, candles, and essential oil diffusers.
- Culinary Uses: Lavender flowers can be used in culinary applications, adding a unique flavor to baked goods, desserts, and teas.
- Medicinal Properties: Lavender has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. It is used in natural remedies for minor burns, insect bites, and skin irritations.
- Landscaping and Decorative Uses: It is excellent for creating borders, hedges, and focal points in gardens. Its long-lasting blooms and pleasant aroma enhance outdoor spaces.
French lavender vs English lavender
French lavender (Lavandula dentata) and English lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) are two popular species of lavender, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Here’s a comparison between the two:

French Lavender (Lavandula dentata)
- Appearance: French lavender is characterized by its distinctive toothed leaves and larger, more ornamental flower spikes. The flowers are topped with bracts that resemble rabbit ears, giving them a unique and decorative appearance.
- Fragrance: The aroma of French lavender is typically stronger and more camphor-like compared to the sweeter, floral scent of English lavender.
- Hardiness: French lavender is less cold-tolerant than English lavender and prefers warmer climates. It is often grown as an annual or in containers in colder regions.
Uses: French lavender is valued for its ornamental qualities and is often used in landscaping and decorative gardens. The flowers are also used in potpourri and sachets.
English Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia)
- Appearance: It is known for its narrow leaves and compact growth habit. The flowers are smaller and more delicate compared to French lavender, with colors ranging from purple to blue, pink, and white.
- Fragrance: It has a sweeter, more floral fragrance that is highly prized in aromatherapy and perfumery.
- Hardiness: It is more cold-tolerant than French lavender and can withstand harsher winter conditions, making it suitable for a wider range of climates.
- Uses: English lavender is commonly used in culinary applications, aromatherapy, and as an ornamental plant in gardens. It is also prized for its medicinal properties.
In summary, French lavender is known for its ornamental value and strong fragrance, while English lavender is prized for its culinary uses, sweet fragrance, and cold tolerance. Both varieties are beautiful and versatile plants that can add beauty and fragrance to any garden.
FAQs
What is special about English lavender?
It is prized for its sweet, floral scent and is used in aromatherapy for relaxation. It’s also popular in cooking for its delicate flavor. Medicinally, it’s known for its anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties.
Does English lavender need full sun?
Yes, it can thrives in full sun, requiring at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily. It prefers well-draining soil and is tolerant of drought once established, making it an excellent choice for sunny, dry locations in the garden.
Conclusion
English Lavender is a versatile and beneficial plant that offers aesthetic beauty, practical uses, and therapeutic properties. By following the proper growing tips and understanding its care requirements, you can enjoy the myriad benefits that this delightful herb brings to your garden and home. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, it is a rewarding choice that will enrich your gardening experience.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before using any herbal remedies, essential oils, or supplements
I am a passionate herbalist and gardening expert dedicated to sharing the transformative power of medicinal plants. With over a decade of hands-on experience, I have cultivated a deep understanding of natural remedies and sustainable gardening practices.
Driven by a love for nature and holistic wellness, My articles provide practical tips and in-depth knowledge to help you grow and use medicinal plants effectively.
